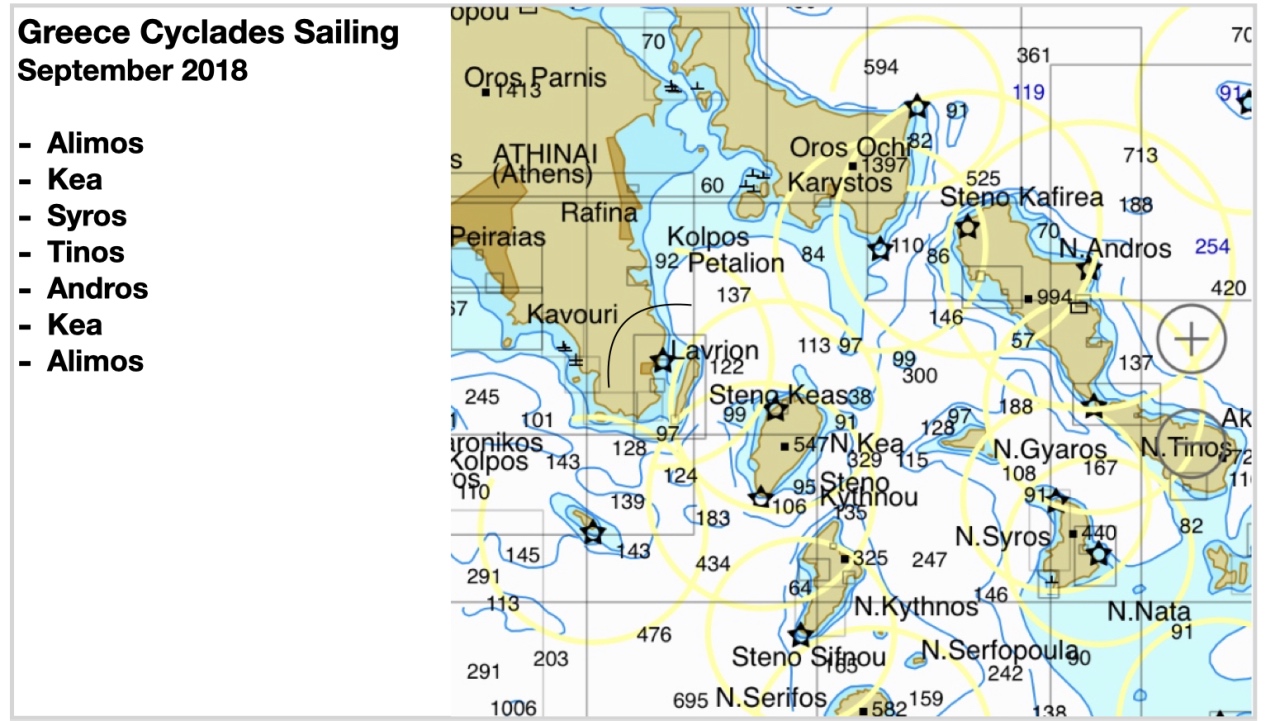
Cyclades
The Cyclades is a group of Greek islands, southeast of the mainland in the Aegean Sea. It centers on uninhabited Delos, considered the birthplace of Apollo, and home to some of Greece's most important archaeological ruins. Many of the islands are popular holiday destinations, known for their beaches, ancient sites, rugged landscapes and traditional blue-and-white stucco towns overlooking the sea.
Area: 2,572 sqkm
Capital: Ermoupoli
The significant Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age Cycladic culture is best known for its schematic, flat sculptures carved out of the islands' pure white marble centuries before the great Middle Bronze Age Minoan civilization arose in Crete to the south. (These figures have been looted from burials to satisfy a thriving Cycladic antiquities market since the early 20th century.)
A distinctive Neolithic culture amalgamating Anatolian and mainland Greek elements arose in the western Aegean before 4000 BCE, based on emmer and wild-type barley, sheep and goats, pigs, and tuna that were apparently speared from small boats (Rutter). Excavated sites include Chalandriani, Phylakopi, Skarkos, Saliagos and Kephala (on Kea) with signs of copperworking, Each of the small Cycladic islands could support no more than a few thousand people, though Late Cycladic boat models show that fifty oarsmen could be assembled from the scattered communities (Rutter), and when the highly organized palace-culture of Crete arose, the islands faded into insignificance, with the exception of Delos, which retained its archaic reputation as a sanctuary throughout antiquity and until the emergence of Christianity, rem.: the start of the dark end).